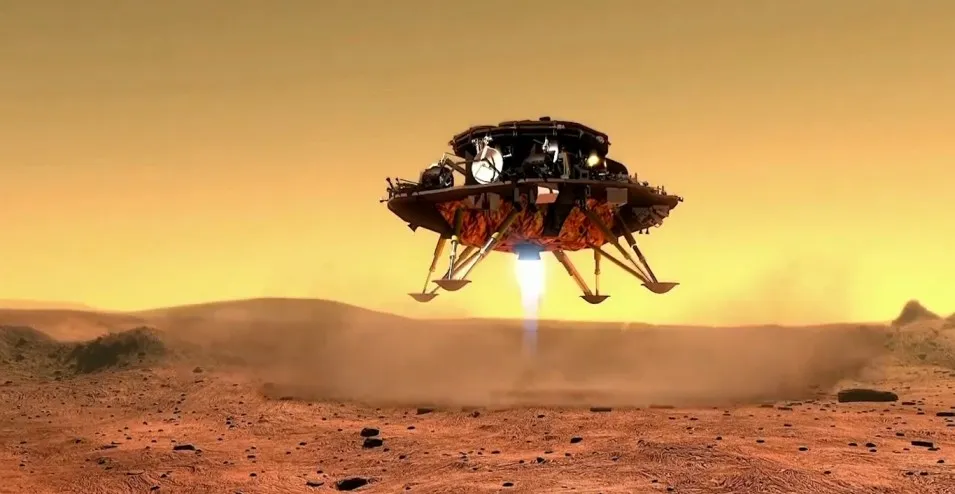
Last year China National Space Administration (CNSA) launched its Tianwen-1 spacecraft to Mars. Now many Chinese affiliated media has confirmed that the lander carrying China’s first Mars rover Zhurong has successfully landed on the Red Planet. Zhurong is designed to operate on Mars for at least 90 Martian days and will now study the red planet’s climate and geology.
The mission makes CNSA the second agency after NASA to successfully land and operate a rover on the Martian surface. This is also China’s first independent journey to Mars. Making the final descent on May 15, the Tianwen’s lander-rover landed on a flat region in the southern part of Utopia Planitia. Before the Tianwen-1 mission, humans have sent more than a dozen spacecraft on Martian soil.
Image showing manmade spacecraft landing site on mars
Tianwen-1 probe was a three-in-one spacecraft that consisted of a lander, an orbiter, and a rover. The probe conducted four trajectory correction maneuvers before it was successfully captured by Mar’s gravity. Before landing the orbiter was separated from the lander and rover. The orbiter will now orbit around Mars for about 687 days (about one Martian year) acting as a medium of communication between the rover and Earth.
Other articles related to Mars exploration
- NASA Perseverance Rover lands on Mars
- NASA's Perseverance Rover first test drive on Mars
- Nasa's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter completed its first test flight on the Martian air

-original.webp)
-original.webp)
-original.webp)



